Anomaly Advisor
The Anomaly Advisor feature lets you quickly surface potentially anomalous metrics and charts related to a particular highlight window of interest.
Getting Started
To enable the Anomaly Advisor you must first enable ML on your nodes via a small config change in netdata.conf. Once the anomaly detection models have trained on the Agent (with default settings this takes a couple of hours until enough data has been seen to train the models) you will then be able to enable the Anomaly Advisor feature in Netdata Cloud.
Enable ML on Netdata Agent
To enable ML on your Netdata Agent, you need to edit the [ml] section in your netdata.conf to look something like the following example.
[ml]
enabled = yes
At a minimum you just need to set enabled = yes to enable ML with default params. More details about configuration can be found in the Netdata Agent ML docs.
Note: Follow this guide if you are unfamiliar with making configuration changes in Netdata.
When you have finished your configuration, restart Netdata with a command like sudo systemctl restart netdata for the config changes to take effect. You can find more info on restarting Netdata here.
After a brief delay, you should see the number of trained dimensions start to increase on the "dimensions" chart of the "Anomaly Detection" menu on the Overview page. By default the minimum num samples to train = 3600 parameter means at least 1 hour of data is required to train initial models, but you could set this to 900 if you want to train initial models quicker but on less data. Over time, they will retrain on up to maximum num samples to train = 14400 (4 hours by default), but you could increase this is you wanted to train on more data.
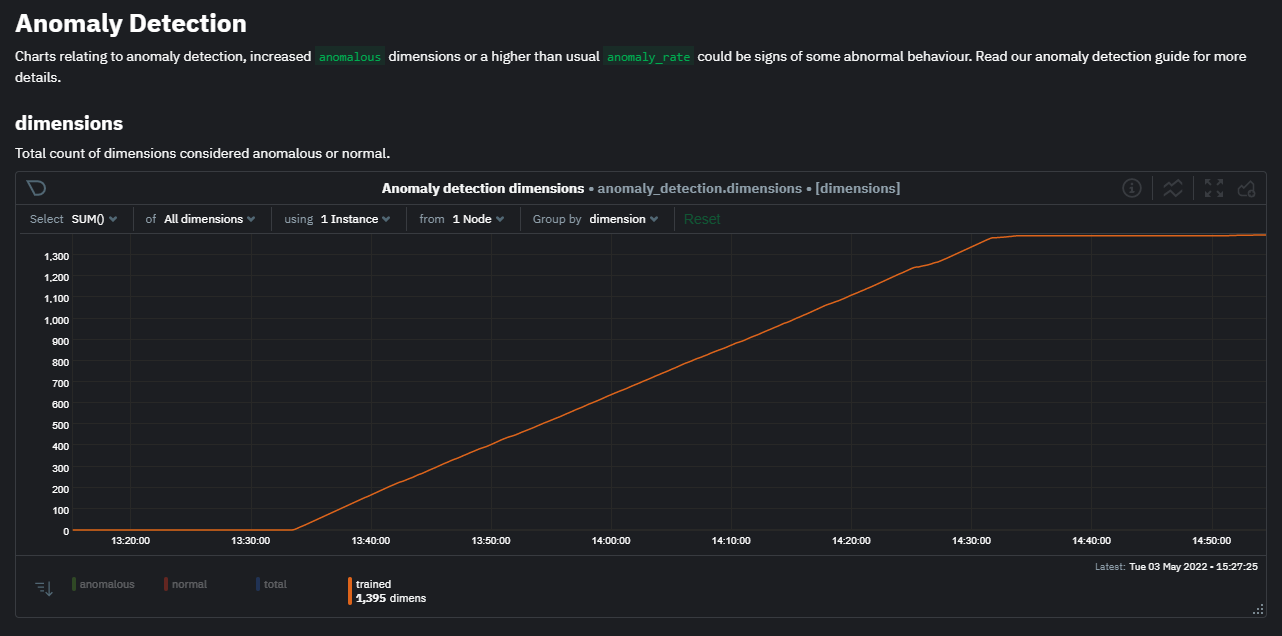
Once this line flattens out all configured metrics should have models trained and predicting anomaly scores each second, ready to be used by the new "anomalies" tab of the Anomaly Advisor.
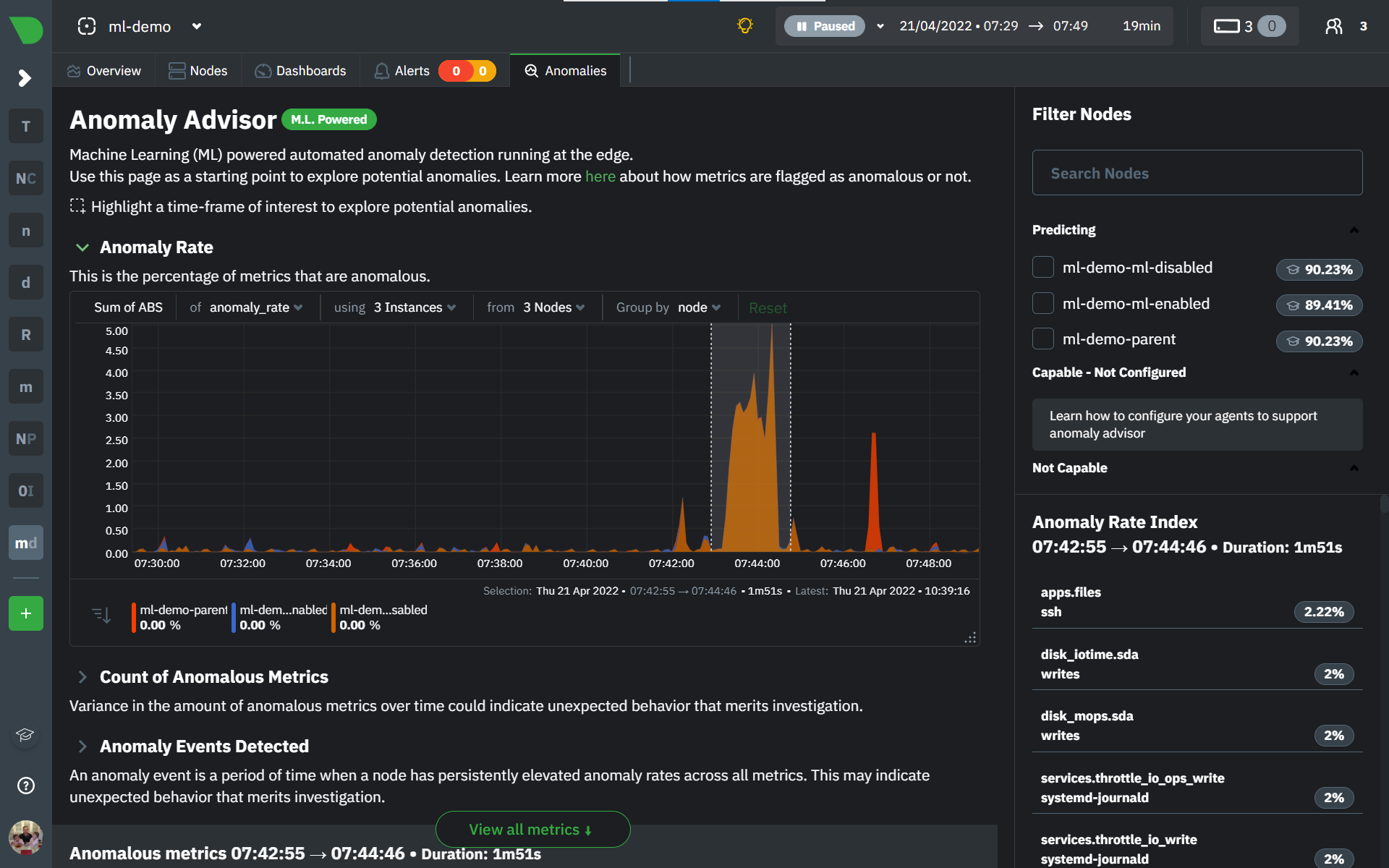
Using Anomaly Advisor
To use the Anomaly Advisor, go to the "anomalies" tab. Once you highlight a particular timeframe of interest, a selection of the most anomalous dimensions will appear below.
The aim here is to surface the most anomalous metrics in the space or room for the highlighted window to try and cut down on the amount of manual searching required to get to the root cause of your issues.
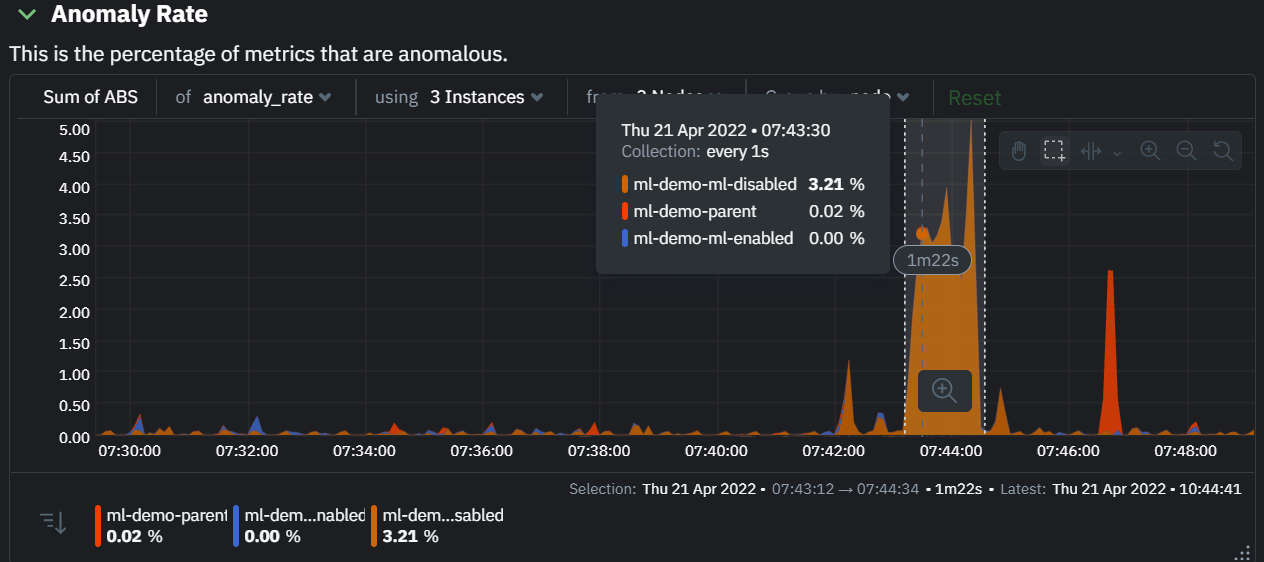
The "Anomaly Rate" chart shows the percentage of anomalous metrics over time per node. For example, in the following image, 3.21% of the metrics on the "ml-demo-ml-disabled" node were considered anomalous. This elevated anomaly rate could be a sign of something worth investigating.
Note: in this example the anomaly rates for this node are actually being calculated on the parent it streams to, you can run ml on the Agent itselt or on a parent the Agent stream to. Read more about the various configuration options in the Agent docs.
The "Count of Anomalous Metrics" chart (collapsed by default) shows raw counts of anomalous metrics per node so may often be similar to the anomaly rate chart, apart from where nodes may have different numbers of metrics.
The "Anomaly Events Detected" chart (collapsed by default) shows if the anomaly rate per node was sufficiently elevated to trigger a node level anomaly. Anomaly events will appear slightly after the anomaly rate starts to increase in the timeline, this is because a significant number of metrics in the node need to be anomalous before an anomaly event is triggered.
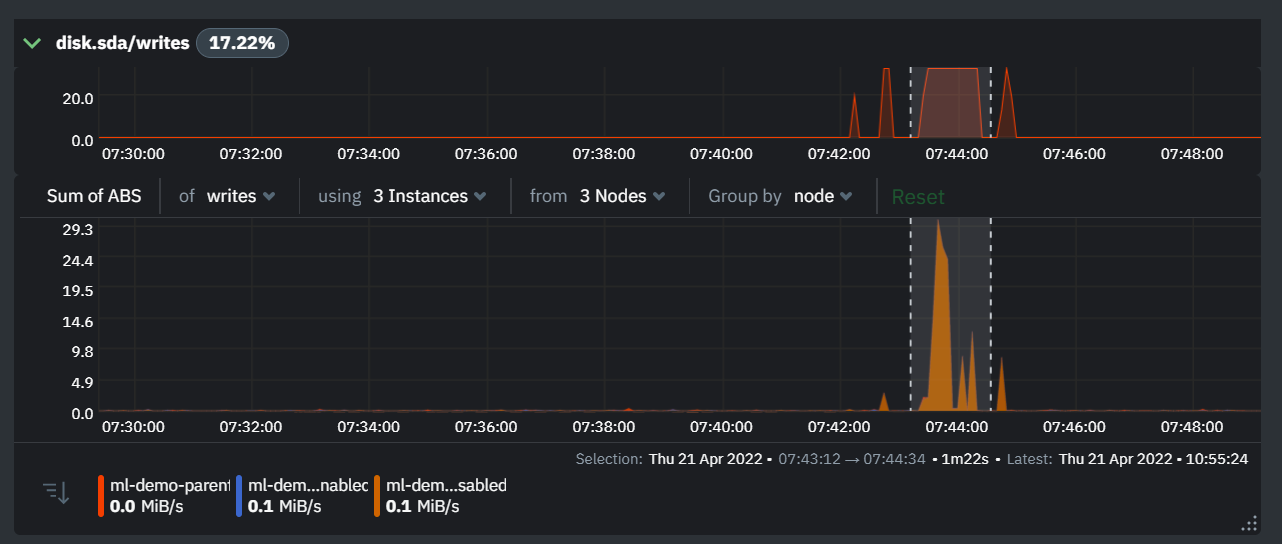
Once you have highlighted a window of interest, you should see an ordered list of anomaly rate sparklines in the "Anomalous metrics" section like below.
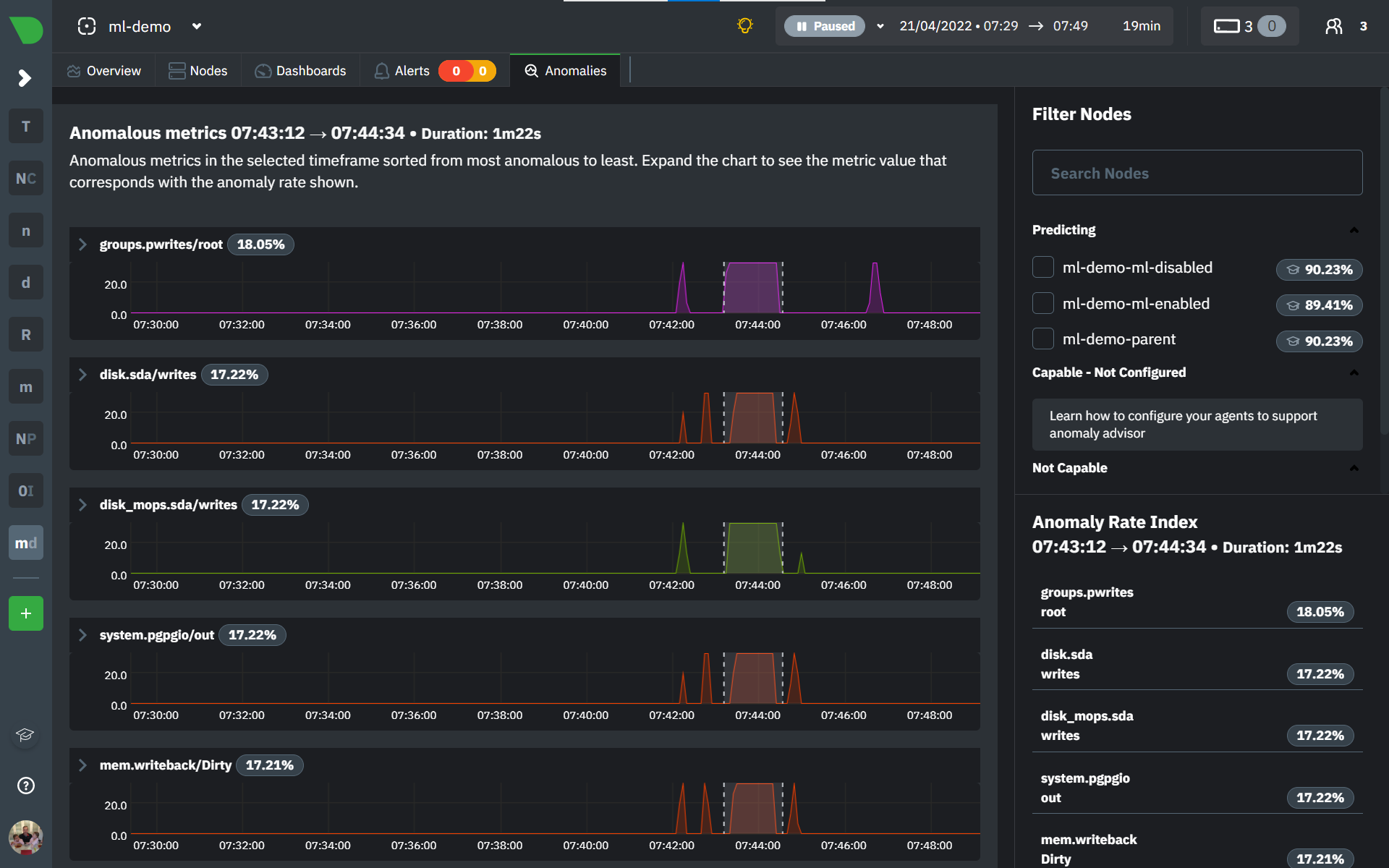
You can expand any sparkline chart to see the underlying raw data to see how it relates to the corresponding anomaly rate.
On the upper right hand side of the page you can select which nodes to filter on if you wish to do so. The ML training status of each node is also displayed.
On the lower right hand side of the page an index of anomaly rates is displayed for the highlighted timeline of interest. The index is sorted from most anomalous metric (highest anomaly rate) to least (lowest anomaly rate). Clicking on an entry in the index will scroll the rest of the page to the corresponding anomaly rate sparkline for that metric.
Usage Tips
- If you are interested in a subset of specific nodes then filtering to just those nodes before highlighting tends to give better results. This is because when you highlight a region, Netdata Cloud will ask the Agents for a ranking over all metrics so if you can filter this early to just the subset of nodes you are interested in, less 'averaging' will occur and so you might be a less noisy ranking.
- Ideally try and highlight close to a spike or window of interest so that the resulting ranking can narrow in more easily on the timeline you are interested in.
You can read more detail on how anomaly detection in the Netdata Agent works in our Agent docs.
🚧 Note: This functionality is still under active development and considered experimental. We dogfood it internally and among early adopters within the Netdata community to build the feature. If you would like to get involved and help us with feedback, you can reach us through any of the following channels:
- Email us at analytics-ml-team@netdata.cloud
- Comment on the beta launch post in the Netdata community
- Join us in the 🤖-ml-powered-monitoring channel of the Netdata discord.
- Or open a discussion in GitHub if that's more your thing
Was this page helpful?
Need further help?
Search for an answer in our community forum.
Contribute
- Join our community forum
- Learn how to contribute to Netdata's open-source project
- Submit a feature request